Breaking Down Hydropower: The Basics for Beginners
Hydropower is a renewable source of energy that has been utilized for centuries to generate electricity. Understanding the basics of hydropower is essential for anyone interested in renewable energy sources. In this beginner’s guide, we will break down the key concepts and processes involved in hydropower generation.
The Basics of Hydropower
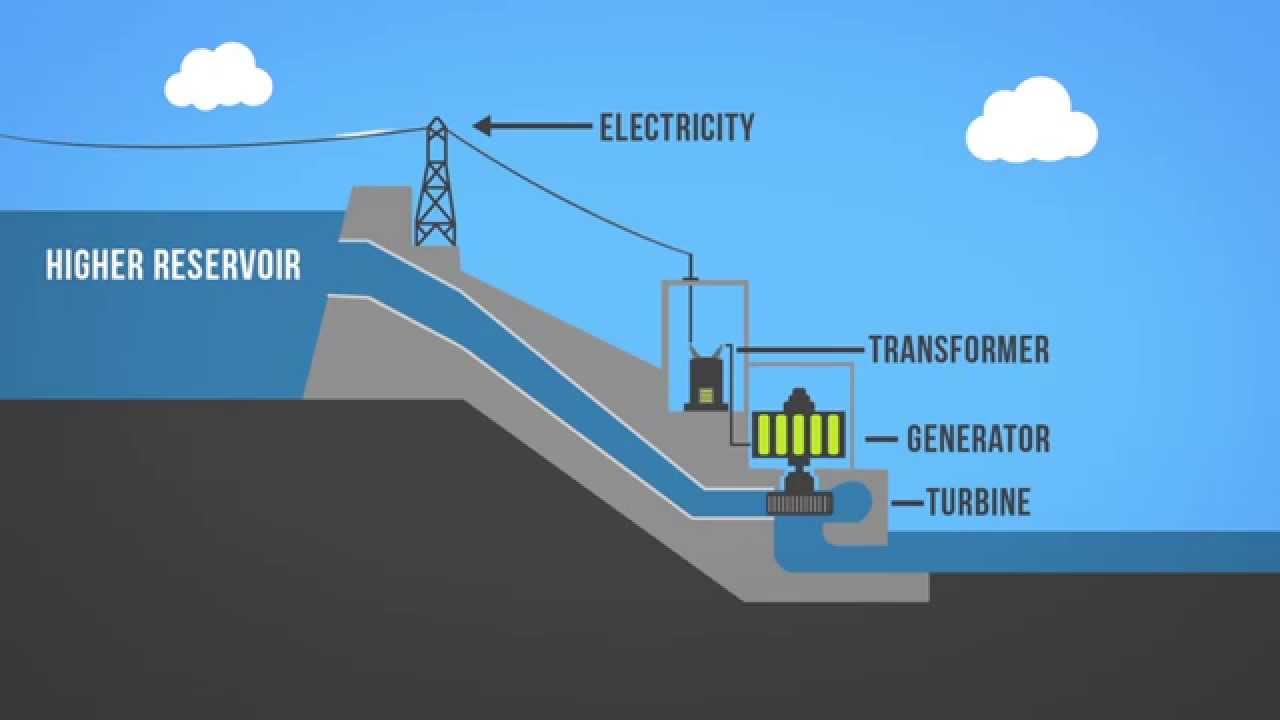
Hydropower is the process of converting the energy of flowing water into electricity. This is typically done by constructing a dam on a river to create a reservoir, which then releases water through turbines to generate power. The force of the flowing water turns the turbines, which in turn rotate a generator to produce electricity.
Types of Hydropower Systems
There are two main types of hydropower systems: conventional and pumped-storage. Conventional hydropower systems use the natural flow of water to generate electricity, while pumped-storage systems store excess electricity by pumping water uphill to be released later for power generation when needed.
Benefits of Hydropower
Hydropower offers several advantages as a renewable energy source. It is a clean and sustainable source of energy that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, hydropower is reliable and can provide a consistent source of electricity, making it a valuable asset for meeting energy demands.
Challenges of Hydropower
While hydropower has many benefits, there are also challenges associated with its implementation. One of the main concerns is the environmental impact of dam construction, which can disrupt local ecosystems and habitats. Additionally, changes in water flow patterns can affect downstream areas and wildlife.
Future of Hydropower
The future of hydropower lies in innovation and sustainability. Researchers are exploring new technologies and methods to improve the efficiency and environmental impact of hydropower systems. By integrating hydropower with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, we can create a more resilient and diverse energy grid.
Understanding Hydropower Generation
Hydropower generation involves several key components that work together to convert the energy of flowing water into electricity. Let’s explore the process in more detail:
1. Dam Construction
The first step in hydropower generation is the construction of a dam on a river. The dam creates a reservoir of water that can be released in controlled amounts to generate power. The height of the dam determines the potential energy that can be harnessed from the flowing water.
2. Turbines and Generators
Once the water is released from the reservoir, it flows through turbines that are connected to generators. The force of the flowing water turns the turbines, which in turn rotate the generator to produce electricity. The amount of electricity generated depends on the flow rate of the water and the size of the turbines.
3. Transmission and Distribution
After electricity is generated, it is transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and other facilities. The electricity grid distributes the power to where it is needed, ensuring a reliable supply of electricity to consumers. Excess electricity can also be stored or sold back to the grid.
The Importance of Hydropower in the Energy Sector
Hydropower plays a crucial role in the energy sector as a reliable and renewable source of electricity. Its ability to generate power consistently makes it an essential component of a balanced energy mix. By understanding the basics of hydropower generation, we can appreciate its significance in meeting our energy needs sustainably.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydropower is a valuable source of renewable energy that offers numerous benefits to society. By harnessing the power of flowing water, we can generate electricity in a clean and sustainable way. As technology advances and new innovations emerge, the future of hydropower looks promising in contributing to a more sustainable energy future.

